The Mediterranean diet is inspired by the eating habits of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea. It emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and moderate consumption of fish, poultry, and dairy products. It limits red meat, refined sugars, and processed foods.
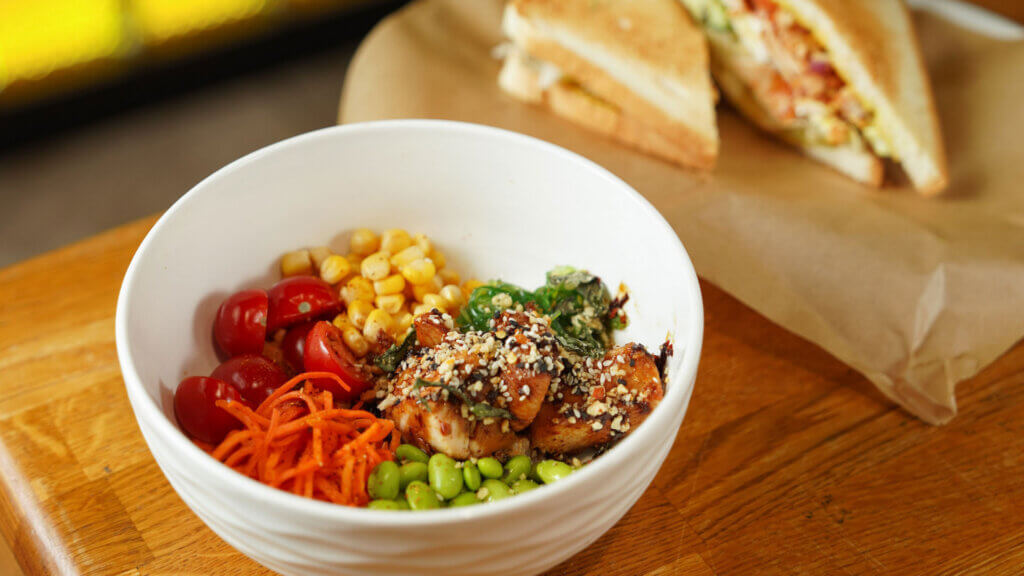
The Mediterranean diet is renowned for its health benefits and is inspired by the traditional eating patterns of countries like Greece, Italy, and Spain. This diet emphasizes the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods that are rich in nutrients. Fruits and vegetables, including tomatoes, leafy greens, citrus fruits, and colorful produce, are staples of the Mediterranean diet, providing a wide array of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Whole grains such as whole wheat, barley, and bulgur are commonly consumed, offering fiber, complex carbohydrates, and essential nutrients. Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and beans are excellent sources of plant-based protein, fiber, and minerals. Nuts and seeds, including almonds, walnuts, and flaxseeds, are incorporated for their healthy fats, protein, and omega-3 fatty acids.
Olive oil takes center stage as the primary source of dietary fat in the Mediterranean diet. It provides monounsaturated fats and antioxidants that contribute to heart health. Fish, particularly fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, is a significant protein source and supplies beneficial omega-3 fatty acids. Poultry, eggs, and dairy products are consumed in moderation, while red meat is limited.
The Mediterranean diet promotes the reduction of refined sugars and processed foods. Instead, natural sweeteners like honey or fruits are used sparingly to satisfy sweet cravings. Herbs and spices are utilized to enhance flavor, reducing the need for excessive salt or added sugars.
The Mediterranean diet has been associated with numerous health benefits. Its focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods provides a balanced intake of macronutrients and micronutrients. The high consumption of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains contributes to a rich fiber content, supporting digestive health and promoting a feeling of fullness. The emphasis on healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil and fish, may help reduce the risk of heart disease and inflammation.
Research suggests that the Mediterranean diet is associated with a lower risk of chronic conditions like cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and cognitive decline. It is also recognized for its positive impact on weight management, as it encourages mindful eating and a balanced approach to food.
It’s important to note that the Mediterranean diet is not a strict set of rules but rather a flexible and adaptable approach to eating. It can be personalized based on individual preferences, cultural considerations, and dietary needs. Consulting with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide further guidance on implementing the Mediterranean diet and tailoring it to specific goals and health conditions.